Scientist Reveal Working Mechanisms of Li based Anodes
2022-11-08编辑:徐红霞
With increasing demand in electric vehicles, grid storage, and portable electronics, the next-generation batteries of higher energy density and improved cycling life are in need. Lithium (Li) metal is considered as one of the most promising candidates to replace the current carbon-based negative electrodes in commercial Li-ion batteries.
However, the practical application of rechargeable lithium metal batteries (LMBs) still suffers from the long-standing challenges, i.e., safety concerns, low Coulombic efficiency (CE) and poor cycle life. A deeper understanding of the factors playing a crucial role during extended electrochemical cycling is often lacking.
A research team from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) conducted an in-depth research of the working mechanisms of the Li-based anodes under three prevalent strategies. These strategies include the use of Li-Al alloys, polymer coating and anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) membrane attaching.
The researchers found that the characterizations clearly captured the unprecedented morphological evolution of the Li-based anode during the electrochemical cycling.
Furthermore, the results indicated the formation of the "dead" electrochemically generated porous structures regardless of >99% cycling efficiency showed in Li symmetric cells in all three cell configurations.
The study sheds light on further understanding of the morphological evolution of the Li anode under different scenarios. In practice, it also enlightens new research activities that may assist in propelling and strengthening the commercialization of LMBs.
The work was published in ACS Energy Letters.
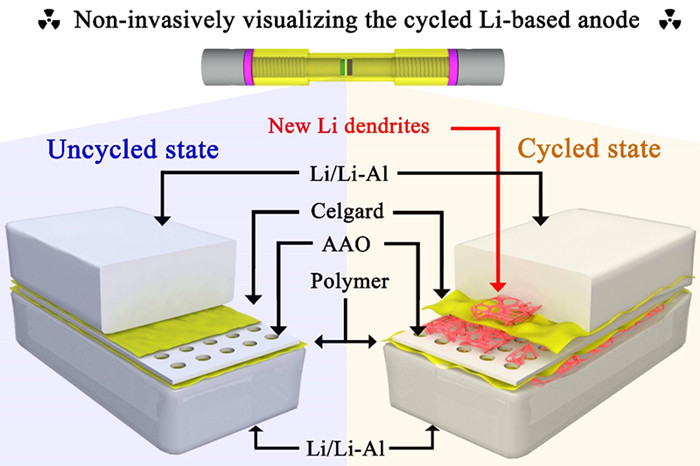
Figure 1 Investigation of the working mechanism of Li-based anodes by synchrotron X-ray imaging (Image by SUN Fu)
(Text by SUN Fu)

